
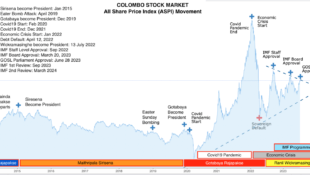
Sri Lanka is facing its worst economic crisis in modern history. Its 22 million strong population is struggling with huge price increases for food, power, medicines and other necessities. That’s if they can get them at all, with private motorists spending hours queuing for their fuel quota.
This is why Sri Lankans have been protesting on the streets and stormed the President’s House.
How did it come to this?
The immediate cause of the crisis is straightforward: Sri Lanka ran out of foreign reserves, the currencies its government and citizens need to pay for imports.
How it got into this situation requires more explanation. It’s a story of fiscal imprudence, unsustainable exchange rate policy and chronic mismanagement.
Running out of foreign currency
Since the beginning of 2020 Sri Lanka’s demand for foreign currency has increased while its ability to earn foreign currency – through exports, loans and other capital inflows – has declined.
This is reflected in the steady decline in official foreign reserves held by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka, falling from about US$8 billion to less than $U2 billion. (The Sri Lankan currency is “closed”, meaning it isn’t traded outside the country, so foreign exchange transactions have to go through the central bank).

As bad these figures are, the reality is worse.
Gross reserves aren’t the same as money in a bank account that can be used for payments. They include, for example, currency already committed to payments, and loans with conditions that limit imports from certain countries.
The actual amount of “usable” foreign currency is less. By early May it was barely US$50 million – a miniscule level for an economy that by the end of 2021 needed about US$75 million a day to pay for imports. This led to Sri Lanka’s government defaulting on a US$78 million interest payment in late May.
Declining currency inflows
Sri Lanka’s declining foreign currency inflows and increasing outflows are due to imports outpacing exports, Sri Lankans overseas sending less money home, the devastation of the tourism sector and higher debt repayments.
In two years Sri Lanka’s annual trade deficit has climbed from about US$6 billion to US$8 billion.

Two other key sources of foreign currency, money sent home by Sri Lankans living abroad and international tourism, were also hit hard.
At their peak, they more than offset the trade deficit for goods.
But since 2019 the value of remittances has fallen more than 20%. Income from tourism, devastated by the 2019 Easter bombings in which 269 were killed, has dropped almost 90% from its 2018 peak.

Propping up the exchange rate
Ordinarily a nation can avoid running out of foreign currency in two ways.
One way is to borrow money. Sri Lanka, however, was already heavily in debt before this crisis. Successive governments borrowed to finance infrastructure projects and prop up loss-making public utilities. With estimated annual debt service costs of US$10 billion, Sri Lanka is now a bad bet for lenders.
The second, and better, way is a floating exchange rate along the lines of those in Australia, Britain, Japan and the United States.
A floating rate helps to balance trade value because the currency’s value changes according to demand.
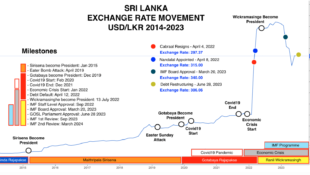
Technically Sri Lanka has a floating currency, but it is a “managed float” – with the government, primarily through the Central Bank of Sri Lanka, pegging and repegging the rupee’s value to the US dollar.
A government can do a number of things to maintain the value its currencies, but the main way is buy the currency itself, using foreign reserves. This is what Sri Lanka’s central bank did.
As foreign reserves ran down, the government adopted other riskier policies. Particularly disastrous was the April 2021 decision to ban fertiliser imports.
This was marketed as a policy to promote organic farming, but really it was about cutting demand for foreign currency.
The subsequent drop in agricultural production has only compounded the economic crisis.
Rising prices
Just as short-term solutions can create longer-term problems, so too can long-term solutions mean short-term pain.
Allowing the (pegged) rupee to depreciate more than 40% against the US dollar has pushed up inflation to 54%.

The help the Sri Lankan government is seeking from the International Monetary Fund is likely to hit people hard, at least initially.
Based on past experience, the IMF will want major commitments on government expenditure and other economic indicators before bailing out Sri Lanka.
But without action, life in Sri Lanka looks even more grim.
With shortages of imported raw materials, industrial output will shrink, creating a downward spiral of low output, low investment, and resultant low economic growth.

On the other hand, Sri Lanka has some natural advantages – from its natural beauty to the most literate population in South Asia. What it needs now is principled political leadership, competent economic management and the right policies.
Thilak Mallawaarachchi is Honorary Associate Professor, Risk and Sustainable Management Group, at The University of Queensland. John Quiggin is Professor at School of Economics, The University of Queensland.
This article first appeared on The Conversation.
https://scroll.in/article/1029077/five-graphs-that-explain-how-sri-lanka-ran-out-of-money
 would enable you to enjoy an array of other services such as Member Rankings, User Groups, Own Posts & Profile, Exclusive Research, Live Chat Box etc..
would enable you to enjoy an array of other services such as Member Rankings, User Groups, Own Posts & Profile, Exclusive Research, Live Chat Box etc.. 
 Home
Home














No Comment.