The Insurance sector is dominated by six companies in terms of total assets of the sector. Out of twenty-seven insurance companies in the sector, six companies contributed to 76.7 per cent of the total assets of the sector at end June 2022. In addition, 71.1 per cent of the market share based on total assets was dominated by the long term insurance sub sector at end June 2022. High concentration in terms of institution poses additional risks as any vulnerability in a large company could significantly affect the sector.
The insurance sector, which faced headwinds and heightened uncertainties in its business expansion, grew at a slower rate in terms of total assets during the first half of 2022. The total asset base of the sector increased by Rs. 65.8 billion, recorded an expansion of 7.9 per cent y-o-y at end June 2022 compared to the asset growth of 10.8 per cent reported during the corresponding period of 2021. Adverse business conditions and decline in disposable income level of households negatively affected the expansion of the insurance sector during the period under consideration.
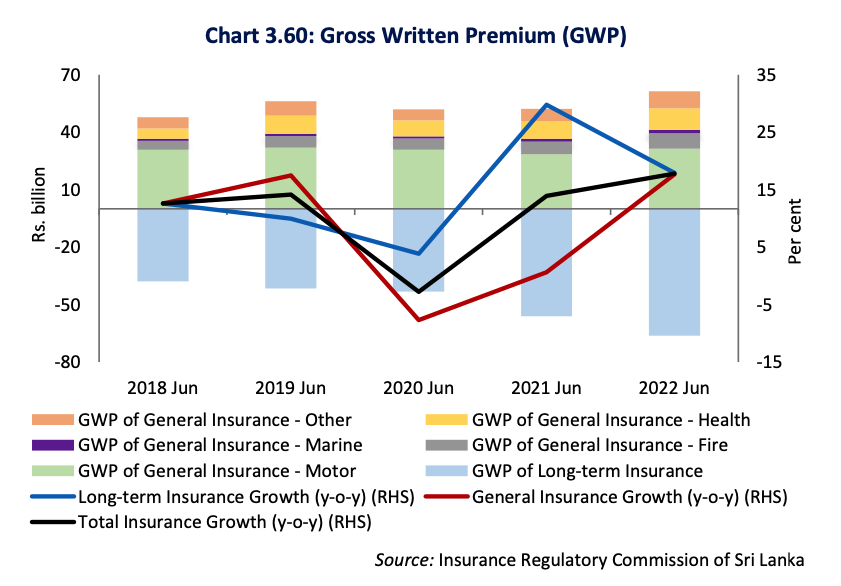
Growth of the Insurance Sector
Growth of GWP of the Insurance sector accelerated during the period under consideration. The Insurance sector as a whole recorded a growth of 17.8 per cent in GWP during the first half of 2022, which is an increase compared to the growth of 13.9 per cent reported during the corresponding period of 2021. GWP of both long term and general insurance sub sectors increased by 17.9 per cent and 17.7 per cent y-o-y, respectively, during the first half of 2022 compared to the growth of 29.8 per cent and 0.7 per cent, respectively, during the first half of 2021. When considering sub sectors of the general insurance, health insurance being the second largest sub sector of the general insurance, recorded the highest growth in GWP of 23.7 per cent during the first half of 2022. However, it was observed that the growth of GWP of the motor insurance sub sector, the largest sub sector, reported a growth of 10.0 per cent during the period under consideration mainly due to the surge in vehicle prices in the secondary market and increased usage of vehicles in the post lockdown periods.
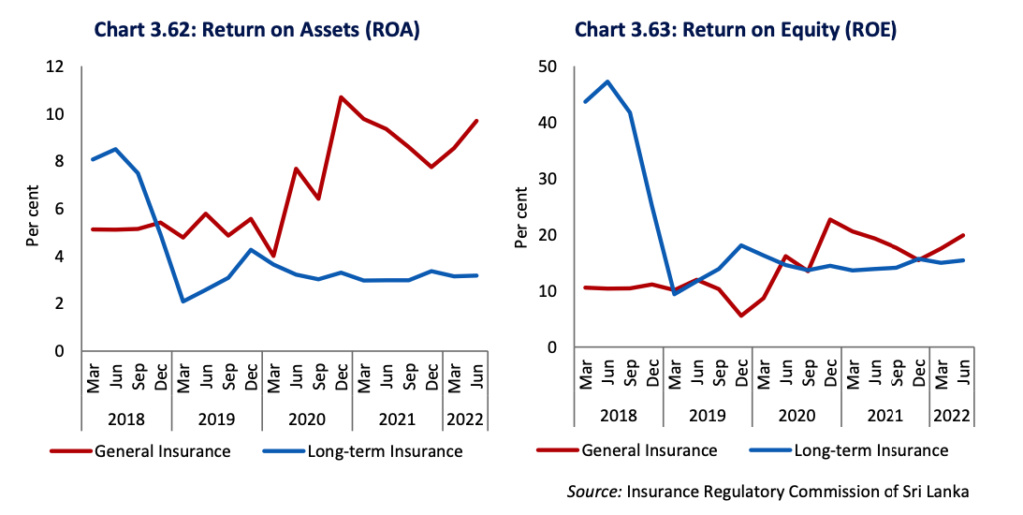
Profitability of the Insurance Sector
The profits of the sector increased during the first half of 2022 compared to the corresponding period of the last year. The Profit Before Tax (PBT) of the sector grew by 33.3 per cent during the first half of 2022 compared to the negative growth of 7.2 per cent during the corresponding period of 2021. This was mainly due to accelerated growth of PBT of the general insurance sub sector which contributed to 66.8 per cent of the Insurance sector profits. PBT of the general insurance sub sector increased to its highest level in 5 years and recorded 66.9 per cent y-o-y growth at the end June 2022. Meanwhile, PBT of the long term insurance sub sector declined by 5.1 per cent during this period. Further, it was observed that around 80.0 per cent of market players in the Insurance sector reported profits during the period under consideration while the rest of the companies made losses.
Profitability of the Insurance sector increased as indicated by ROA and ROE for the period under review. ROA and ROE of the general insurance sub sector increased to 9.7 per cent and 19.9 per cent, respectively, at end June 2022 from 9.4 per cent and 19.3 per cent recorded at end June 2021. Meanwhile, ROA and ROE of the long term insurance sub sector also increased to 3.2 per cent and 15.4 per cent, respectively, at end June 2022 from 3.0 per cent and 13.9 per cent recorded at end June 2021.
Claims made by the Insurance sector increased, while a decrease in investment income was observed during the first half of 2022. Total claims made by the long term insurance sub sector, which includes maturity and death benefits, increased by 22.1 per cent, whereas the claims made by the general insurance sub sector recorded a y-o-y growth of 30.4 per cent. Meanwhile, the investment income of the sector decreased by 8.6 per cent for the first half of 2022 compared to the growth of 10.7 per cent during the corresponding period of 2021 mainly due to the decelerated investment income recorded by the long term insurance sub sector. However, investment income is expected to increase in the coming period as investments in high yield government securities have increased.
CAR of both the long term insurance sub sector and the general insurance sub sector declined during the period under consideration, though the sector maintained CAR above the minimum requirement of 120 per cent11. CAR of long term insurance sub sector and general insurance sub sector considerably declined to 282.0 per cent and 209.0 per cent, respectively, at end June 2022 compared to 351.0 per cent and 293.0 per cent, respectively, recorded at end the of the corresponding period of 2021. The Insurance sector may face various risks such as market risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk, and risks emanating from adverse shocks such as natural calamities and economic downturns. Therefore, adequate levels of capital and liquidity are important to withstand possible shocks to the sector. Although the prevailing higher CAR may act as an additional cushion to the sector to withstand the risks to some extent, a significant contraction in the economy could further deteriorate the capital of the sector.
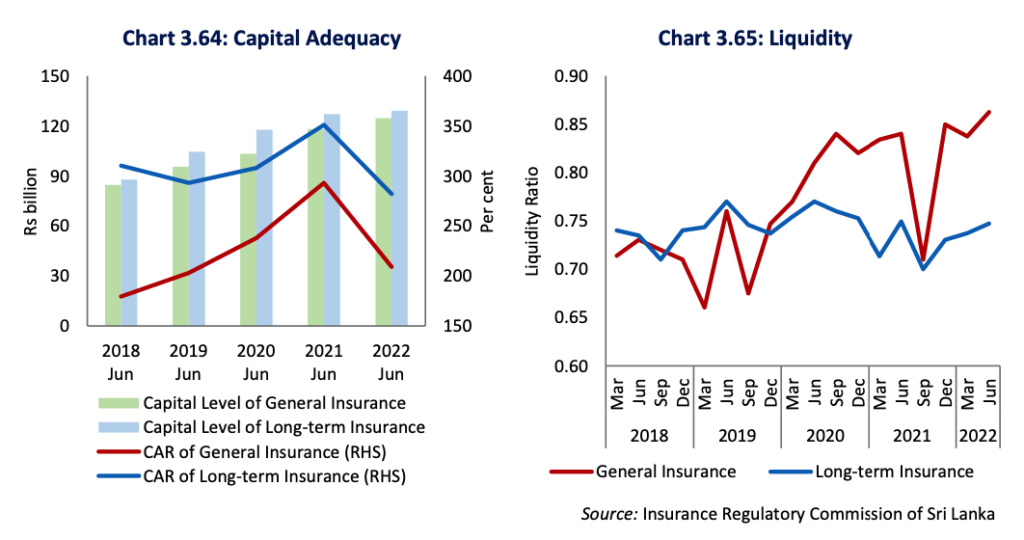
Liquidity ratios of the Insurance sector increased marginally during the period under review. The availability of liquidity is vital for the business continuity of insurance service providers. It was observed that the liquidity ratios of the general insurance sub sector increased marginally to 0.86 per cent at end June 2022 compared to 0.84 per cent at end June 2021 while the liquidity ratios of the long term insurance sub sector remained at 0.75 per cent at end June 2022 on par with the ratio recorded at end June 2022 compared to end June 2021.
https://www.cbsl.gov.lk/sites/default/files/cbslweb_documents/publications/fssr/fssr_2022e.pdf
 would enable you to enjoy an array of other services such as Member Rankings, User Groups, Own Posts & Profile, Exclusive Research, Live Chat Box etc..
would enable you to enjoy an array of other services such as Member Rankings, User Groups, Own Posts & Profile, Exclusive Research, Live Chat Box etc.. 
 Home
Home
















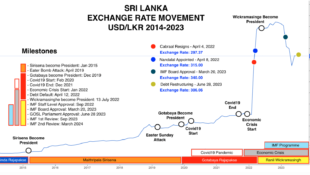
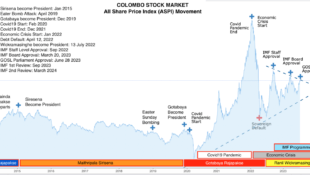

No Comment.